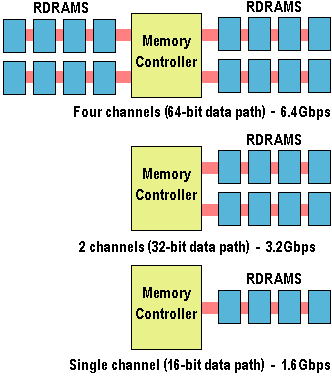
Conventional DRAM architectures have reached their practical upper limit in operating frequency and bus width. With mass market CPUs operating at over 300MHz and media processors executing more than … [Continue reading]

Conventional DRAM architectures have reached their practical upper limit in operating frequency and bus width. With mass market CPUs operating at over 300MHz and media processors executing more than … [Continue reading]

Memory chips are generally packaged into small plastic or ceramic dual inline packages (DIPs) which are themselves assembled into a memory module. The single inline memory module or SIMM is a … [Continue reading]

By the end of the millennium, as memory subsystems standardised around an 8-byte data interface, the Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM) had replaced the SIMM as the module standard for the PC … [Continue reading]
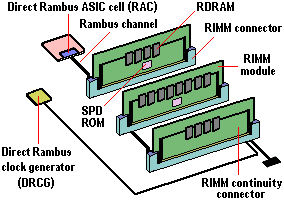
With the introduction of Direct RDRAM (DRDRAM) in 1999 came the RIMM module (the name is not an acronym, but a trademark of Rambus Inc.). RIMM connectors have a form factor similar to DIMMs … [Continue reading]
When a computer system boots up, it must detect the configuration of the memory modules in order to run properly. For a number of years, Parallel Presence Detect (PPD) was the traditional method … [Continue reading]
Memory modules have traditionally been available in two basic flavours: non-parity and parity. Parity checking uses a ninth memory chip to hold checksum data on the contents of the other eight … [Continue reading]
Unlike parity memory, which uses a single bit to provide protection to eight bits, ECC uses larger groupings. Five ECC bits are needed to protect each eight-bit word, six for 16-bit words, seven … [Continue reading]
In recent times, as well as becoming much cheaper, RAM has also become more complicated. There are currently a proliferation of different varieties, shapes and voltages. The first step in planning … [Continue reading]
In the late 1990s, PC users have benefited from an extremely stable period in the evolution of memory architecture. Since the poorly organised transition from FPM to EDO there has been a … [Continue reading]
Flash memory is a solid-state, non-volatile, rewritable memory that works like RAM and a hard-disk drive combined. It resembles conventional memory, coming in the form of discrete chips, modules, or memory cards such as those made by Memory … [Continue reading]
RADSL, like ADSL, operates faster in one direction than in the other and has the same transmission limits as ADSL. But as … [Read More...]
What is Cyber Threat Hunting? Cyber Threat Hunting is the practice of proactively searching through computer networks for advanced threats and … [Read More...]
Since the LCD panels of a projector are too small to apply a colour filter by vapour deposition in the same manner as … [Read More...]