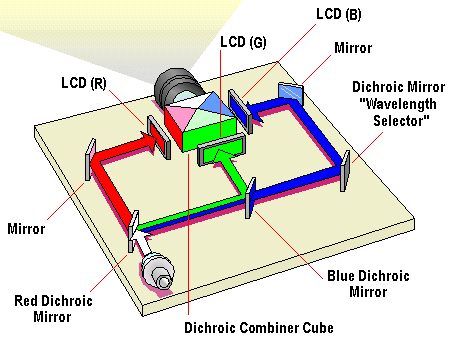
Since the LCD panels of a projector are too small to apply a colour filter by vapour deposition in the same manner as notebook monitors, the light must first of all be split into the three primary colours of red, green and blue.
This task is performed by so-called dichroic (double-refracting) mirrors. These are produced by coating glass with metallic oxides inside a vacuum furnace. Different metallic oxides reflect only a specific part of the light spectrum, while allowing all other light components to pass through. Two dichroic mirrors arranged in series thus split white light into red, green and blue light.
LCD panels are used to block differing amounts of each colour, allowing a total of 16.7 million colours to be produced when the light paths are recombined in a dichroic cube. The recombined light is the launched via the projection lens onto the screen.
The introduction of polysilicon has made it possible to miniaturise the transistor elements in a projector’s LCD panels, enabling both higher light transmission and a reduction in the size. On the 0.9 inch panels of modern XGA projectors, for example, 786,432 pixels are located on the surface area of only 2.5 square centimetres. Since a projector three LCD panels, one for each of the primary colours, it possesses more than 2.36 million pixels which can be activated individually to guarantee absolutely precise rendition down to the smallest detail.
In order to clearly separate the individual pixels, LCD projectors employ a microfine grid to prevent the light from one pixel influencing the adjoining pixel. The light is thus partially absorbed before making impact with the liquid crystal layer, in order to prevent cross-fading. This means that although the grid has a positive effect on picture quality it also entails some loss of light.
High-end projectors compensate for this light loss by incorporating a micro lens array (MLA) in front of the microfine grid. Each of these tiny lenses concentrates the incoming light and directs the entire quantity of light exactly through the matrix, so as to ensure that the minimum possible quantity of light falls on and is absorbed by the grid itself.
As well as increasing luminous efficiency from between 50% to 70%, micro lens technology also minimises a type of pixelisation that afflicts LCD projectors. When a projector’s lens is sharply focused each individual pixel can appear on the screen as though in its own little black box. The lines of the boxes are where the control electronics stops the light from shining through the panel. It’s somewhat like looking at the scenery through a fly screen, and is thus referred to as the screen door effect.
Contrast levels on LCD projectors are determined by how efficient they are at blocking off light. This has to be done by each of the three LCD panels. The result is an image that has dark grey blacks rather than black blacks. This problem is of more relevance to video than to data applications.
Other issues with LCD projectors are:
- Their susceptibility to heat; the organic compounds used in LCD filters – in particular the blue – can be broken down by excess heat, resulting in a degradation of image quality.
- Dead Pixels; pixels can become permanently on or permanently off, and while this is barely noticeable with one dead pixel, the presence of multiple dead pixels can be a irritation.
On the plus side, LCD projectors are the elder statesmen of digital projection; they’ve been around for longer than rival technologies. The actual LCD panels are made by several companies – including Sony and Epson – and these are then incorporated into many different manufacturers’ designs. A consequence is wide availability and – especially for mid-level projectors – competitive prices.
Historically, LCD projectors delivered better colour saturation than the rival DLP technology. The principal reason for this was the inclusion of a clear segment in the colour wheel of early single-chip DLP projectors. While this had the effect of making the image is brighter than it would otherwise be, it also tended to reduce colour saturation. The advent of six-segment colour wheels in DLP projectors has significantly reduced LCD technology’s advantage in this area.
Another advantage of LCD is its superior light-efficiency. For a given lamp wattage, an LCD projector will generally have a higher ANSI lumens rating than a DLP projector. This enables LCD technology to compete extremely well in situations where high light output is required.
When the first portable LCD projectors appeared in 1993, they used high-temperature polysilicon (HTPS) VGA LCD panels and a small, high-brightness metal-halide lamp. By 2004 the first crop of projectors capable of 2K (1920 x 1080) resolution were coming to market and lumen ratings had reached 3000 and more.
No matter what display resolution is available, customers will always want more pixels on the screen. While research and development efforts will continue, it appears that we may be close to reaching the performance limit for transmissive LCD technology. The trend away from transmissive imaging technologies looks to be firmly established, and tomorrow’s higher-resolution projectors are likely to be based on reflective imaging technologies such as DLP and LCOS.