Conventional DRAM architectures have reached their practical upper limit in operating frequency and bus width. With mass market CPUs operating at over 300MHz and media processors executing more than 2 GOPs, it is clear that their external memory bandwidth of approximately 533 MBps cannot meet increasing application demands. The introduction of Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM) in 1999 is likely to prove one of the long term solutions to the problem.
Direct RDRAM is the result of a collaboration between Intel and a company called Rambus to develop a new memory system. It is a totally new RAM architecture, complete with bus mastering (the Rambus Channel Master) and a new pathway (the Rambus Channel) between memory devices (the Rambus Channel Slaves). Direct RDRAM is actually the third version of the Rambus technology. The original (Base) design ran at 600MHz and this was increased to 700MHz in the second iteration, known as Concurrent RDRAM.
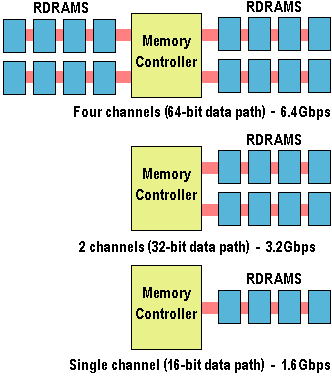
A Direct Rambus channel includes a controller and one or more Direct RDRAMs connected together via a common bus – which can also connect to devices such as micro-processors, digital signal processors (DSPs), graphics processors and ASICs. The controller is located at one end, and the RDRAMS are distributed along the bus, which is parallel terminated at the far end. The two-byte wide channel uses a small number of very high speed signals to carry all address, data and control information at up to 800MHz. The signalling technology is called Rambus Signalling Logic. Each RSL signal wire has equal loading and fan-out is routed parallel to each other on the top trace of a PCB with a ground plane located on the layer underneath. Through continuous incremental improvement signalling data rates are expected to increase by about 100MHz a year to reach a speed of around 1000MHz by the year 2001.
At current speeds a single channel is capable of data transfer at 1.6 GBps and multiple channels can be used in parallel to achieve a throughput of up to 6.4 GBps. The new architecture will be capable of operating at a system bus speed of up to 133MHz.
Problems with both the Rambus technology and Intel’s chipset supporting it – the i820 – delayed DRDRAM’s appearance until late 1999 – much later than had been originally planned. As a result of the delays Intel had to provide a means for the 820 chipset to support SDRAM DIMMs as well as the new Direct RDRAM RIMM module. A consequence of this enforced compromise and the need for bus translation between the SDRAM DIMMs and the 820’s Rambus interface, was that performance was slower than when the same DIMMs were used with the older 440BX chipset! Subsequently, the component which allowed the i820 to use SDRAM was found to be defective and resulted in Intel having to recall and replace all motherboards with the defective chip and to also swap out the SDRAM that had been used previously with far more expensive RDRAM memory!
And Intel’s Rambus woes didn’t stop there. The company was repeatedly forced to alter course in the face of continued market resistance to RDRAM and AMD’s continuing success in embracing alternative memory technologies. In mid-2000, its 815/815E chipsets were the first to provide support for PC133 SDRAM and a year later it revealed that its forthcoming i845 chipset would provide support for both PC 133 SDRAM and DDR-DRAM on Pentium 4 systems.
- What is Level 1 (L1) Cache Memory?
- What is L2 (Level 2) cache memory?
- RAM or Main Memory – PC / computer memory (DIMM, DRAM, SDRAM)
- DRAM – Dynamic Random Access Memory
- FPM DRAM
- EDO (Extended Data Out) and BEDO (Burst Extended Data Out) DRAM
- SDRAM
- PC133 SDRAM
- DDR SDRAM explained
- DDR2 DRAM
- Dual Channel DDR Memory
- 1T SRAM
- Direct DRAM
- SIMMs
- DIMM Memory
- RIMMs Memory
- Memory Presence Detection
- Parity Memory
- ECC Memory
- Memory Upgrades
- The Evolution of Memory
- Flash Memory
- Magnetic RAM