Launched in mid-1997, the Pentium II introduced a number of major changes to the processing end of the PC:
- First, the chip itself and the system’s Level 2 cache are connected by a dedicated bus which can run simultaneously with the processor-to-system bus.
- Second, the processor, secondary cache and heatsink are all mounted on a small board that plugs into a slot on the motherboard, in a way more reminiscent of an add-in card than a traditional processor/socket arrangement. Intel has christened this the Single Edge Contact cartridge (SEC).
- The third change is more of a synthesis really, as Pentium II unites the Dual Independent Bus (DIB) feature of the Pentium Pro with the MMX enhancements found on Pentium MMX processors to form a new kind of Pentium Pro/MMX hybrid. Consequently, whilst looking very different to previous Intel processors, internally the Pentium II is a mixture of new technologies and enhancements to old ones.
Unlike the Pentium Pro, which operates at 3.3V, the Pentium II operates at 2.8 V, thereby allowing Intel to run it at higher frequencies without unduly increasing its power requirements. While a 200MHz Pentium Pro with a 512KB cache consumes about 37.9 watts of power, a 266-MHz Pentium II with a 512KB cache burns 37.0 W.
Like the Pentium Pro, the Pentium II utilises Intel’s Dynamic Execution Technology. As software instructions are read into the processor and decoded, they’re entered into an execution pool. Dynamic Execution Technology adopts three main approaches to optimising the way in which the processor deals with that code. Multiple Branch Prediction examines the program flow along several branches and predicts where the next instruction will be found in memory.
As the processor reads, it’s also checking out instructions further down the pipeline, accelerating workflow as a result. Data Flow Analysis optimises the sequence in which instructions will be executed, by examining decoded instructions and determining whether they’re ready for processing or if they’re dependent on other instructions. Speculative Execution increases the speed that instructions are dealt with by looking ahead of the current instruction and processing further instructions that are likely to be needed. These results are then stored as speculative results until the processor knows which are needed and which aren’t. At this point the instructions are returned to their normal order and added to the flow.
There are two basic benefits of Dynamic Execution Technology: Instructions are processed more quickly and efficiently than usual and, unlike CPUs utilising RISC architecture, programs don’t have to be recompiled in order to extract the best from the processor. The CPU does all the work on the fly.
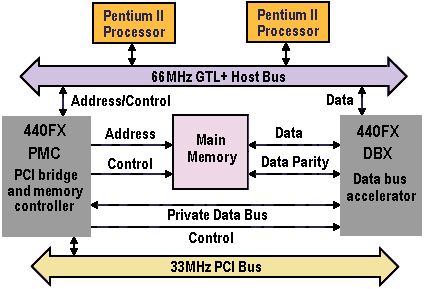
The Pentium II employs a gunning-transceiver-logic (GTL+) host bus that offers glueless support for two processors. At the time of its launch, this provided a cost-effective, minimalist two-processor design that allows symmetric multiprocessing (SMP). The two-processor limitation was not imposed by the Pentium II itself, but by the supporting chipset. Initially limiting the chipset to a dual-processor configuration, allowed Intel and workstation vendors to offer dual-processor systems in a more timely and economical manner than would otherwise have been possible. The limitation was removed in mid-1998 with the release of the 450NX chipset, supporting 1- to 4-way processor operation. The 440FX chipset, comprising PMC and DBX chips, does not offer memory interleaving, but does support EDO DRAM, allowing improved memory performance by reducing clock latencies.
When Intel designed the Pentium II, it also tackled the poor 16-bit performance of its forefather. The Pentium Pro is superb at running fully 32-bit software such as Windows NT, but fell behind even the standard of the Pentium when running 16-bit code. This meant worse than Pentium performance under Windows 95, large parts of which are still 16-bit. Intel solved this problem by using the Pentium’s segment descriptor cache in the Pentium II.
Like the Pentium Pro, the Pentium II is extremely fast for floating point arithmetic. Along with the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) this will make the Pentium II a powerful solution for high-performance 3D graphics.
- Pentium Architecture
- Pentium Pro
- Pentium MMX Technology
- Pentium II
- Pentium SEC
- Pentium “Deschutes
- Pentium Xeon
- Pentium III
- Pentium Tualatin
- Pentium 4
- Pentium Northwood
- Hyper-Threading Technology
- Pentium Prescott
- Pentium Processor Numbers
- Multi-Core Processors
- Pentium Smithfield
- Pentium D
- Pentium Roadmap
PentiumII were great processors and still are today !
You can do whatever u want with PII: office, internet, audio editing, video editing, dvd playback(PII350 or above) and play fantastic games from those years 2001/2002,..