Resolution is a term often used interchangeably with addressability, but it more properly refers to the sharpness, or detail, of the visual image. It is primarily a function of the monitor and is determined by the beam size and dot pitch (sometimes referred to as line pitch). An image is created when a beam of electrons strikes phosphors which coat the base of the monitor’s screen. A group comprising one red, one green and one blue phosphor is known as a pixel. A pixel represents the smallest piece of the screen that can be controlled individually, and each pixel can be set to a different colour and intensity. A complete screen image is composed of thousands of pixels and the screen’s resolution – specified in terms of a row by column figure – is the maximum number of displayable pixels. The higher the resolution, the more pixels that can be displayed and therefore the more information the screen can display at any given time.
Resolutions generally fall into predefined sets and the table below shows the series of video standards since CGA, the first to support colour/graphics capability:
| Date | Standard | Description | Resolution | No. colours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 | CGA | Colour Graphics
Adapter |
640×200
160×200 |
None
16 |
| 1984 | EGA | Enhanced Graphics
Adapter |
640×350 | 16 from 64 |
| 1987 | VGA | Video Graphics
Array |
640×480
320×200 |
16 from 262,144
256 |
| 1990 | XGA | Extended Graphics Array | 1024×768 | 16.7 million |
| SXGA | Super Extended Graphics Array | 1280×1024 | 16.7 million | |
| UXGA | Ultra XGA | 1600×1200 | 16.7 million |
The lack of a widely accepted standard for >VGA pixel addressabilities was a problem for manufacturers, system builders, programmers and end users alike. The matter was addressed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) – a consortium of video adapter and monitor manufacturers whose goal is to standardise video protocols – who developed a family of video standards that were backward compatible with VGA but offered greater resolution and more colours. For a while – prior to the emergence of the XGA family of definitions – VESA’s VGA BIOS Extensions (collectively known as Super VGA) were the closest thing to a standard.
Typically, an SVGA display can support a palette of up to 16.7 million colours, although the amount of video memory in a particular computer may limit the actual number of displayed colours to something less than that. Image-resolution specifications vary. In general, the larger the diagonal screen measure of an SVGA monitor, the more pixels it can display horizontally and vertically. Small SVGA monitors (14in diagonal) usually use a resolution of 800×600 and the largest (20in+ diagonal) can display 1280×1024, or even 1600×1200, pixels.
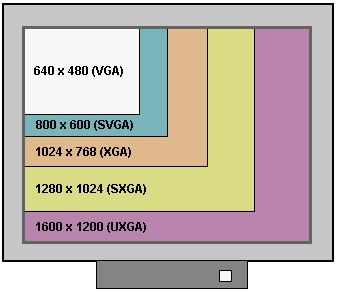
XGA was developed by IBM and was originally used to describe proprietary graphics adapters designed for use in Micro Channel Architecture expansion slots. It has subsequently become the standard used to describe cards and displays capable of displaying resolutions up to 1024×768 pixels.
VESA’s SXGA standard is used to describe the next screen size up – 1280×1024. SXGA is notable in that its standard ratio is 5:4, while VGA, SVGA, XGA and UXGA are all the traditional 4:3 aspect ratio found on the majority of computer monitors.
Pixels are smaller at higher resolutions and prior to Windows 95 – and the introduction of scaleable screen objects – Windows icons and title bars were always the same number of pixels in size whatever the resolution. Consequently, the higher the screen resolution, the smaller these objects appeared – with the result that higher resolutions worked much better on physically larger monitors where the pixels are correspondingly larger. These days the ability to scale Windows objects – coupled with the option to use smaller or larger fonts – affords the use far greater flexibility, making it perfectly possible to use many 15in monitors at screen resolutions of up to 1024×768 pixels and 17in monitors at resolutions up to 1600×1200.
The table below identifies the various SVGA standards and indicates appropriate monitor sizes for each:
| 800×600 | 1024×768 | 1152×882 | 1280×1024 | 1600×1200 | 1800×1440 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15in | YES | YES | ||||
| 17in | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||
| 19in | YES | YES | YES | |||
| 21in | YES | YES |
All SVGA standards support the display of 16 million colours, but the number of colours that can be displayed simultaneously is limited by the amount of video memory installed in a system. The greater number of colours, or the higher the resolution or, the more video memory will be required. However, since it is a shared resource reducing one will allow an increase in the other.
- How Do Computers Make Pictures?
- Graphic Card Resolution
- Graphic Card Colour Depth
- Graphic Card Components
- Graphic Card Memory
- Graphic Card Driver Software
- 3d Accelerated Graphic Cards
- Graphic Card Geometry
- 3D Rendering
- FSAA Graphic Card Technology
- Digital Graphic Cards
- DVI Graphic Cards
- HDCP Technology
- Graphic Card HDMI Ports
- Graphic Card Display Port
- Unified Display Special Interest Group
- DirectX
- OpenGL technology
- Direct3D
- Talisman
- Fahrenheit Graphic Cards
- SLI Technology
- CrossFire Graphic Cards