It was at the Intel Development Forum in March 2006 that Intel released details of its new Intel Core microarchitecture, the successor to the NetBurst and mobile Pentium M architectures and foundation for the company’s forthcoming multi-core server, desktop and mobile processors.
Building on the power-saving philosophy begun with the Mobile Intel Pentium M processor microarchitecture and existing Intel Pentium 4 processor technologies, the new microarchitecture features a number of important advances:
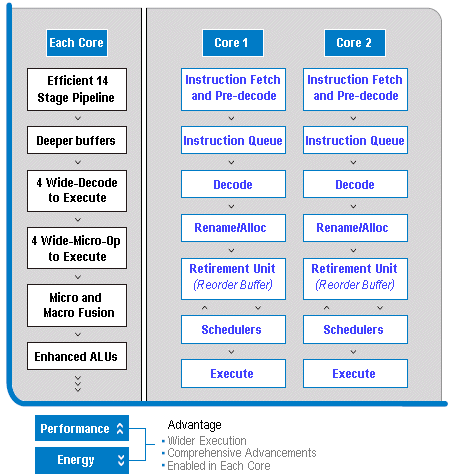
- Intel Wide Dynamic Execution: Delivers more instructions per clock cycle, improving execution and energy efficiency. Every execution core is wider, allowing each core to complete up to four full instructions simultaneously using an efficient 14-stage pipeline.
- Intel Intelligent Power Capability: Includes features that further reduce power consumption by intelligently powering on individual logic subsystems only when required.
- Intel Advanced Smart Cache: This includes a shared L2 cache to reduce power by minimising memory traffic and increase performance by allowing one core to utilise the entire cache when the other core is idle.
- Intel Smart Memory Access: Yet another feature that improves system performance by hiding memory latency and thus optimising the use of data bandwidth out to the memory subsystem.
- Intel Advanced Digital Media Boost: Now many 128-bit SSE, SSE2 and SSE3 instructions execute within only one cycle. This effectively doubles the execution speed for these instructions which are used widely in multimedia and graphics applications.
Dynamic execution is a combination of techniques (dataflow analysis, speculative execution, out of order execution, and super scalar) that Intel first implemented in the P6 microarchitecture used in the Pentium Pro processor, Pentium II processor, and Pentium III processors. For its NetBurst microarchitecture, Intel introduced its Advanced Dynamic Execution engine, a very deep, out-of-order speculative execution engine designed to keep the processor’s execution units executing instructions. It also featured an enhanced branch-prediction algorithm to reduce the number of branch mispredictions.
Now with the Intel Core microarchitecture, Intel significantly enhances this capability with Intel Wide Dynamic Execution, enabling the delivery of more instructions per clock cycle to improve execution time and energy efficiency. Every execution core is wider, allowing each core to fetch, dispatch, execute, and return up to four full instructions (one more than Intel’s previous microarchitectures) simultaneously. Further efficiencies include more accurate branch prediction, deeper instruction buffers for greater execution flexibility, and additional features to reduce execution time.
One such feature is macrofusion. In previous generation processors, each incoming instruction was individually decoded and executed. Macrofusion enables common instruction pairs (such as a compare followed by a conditional jump) to be combined into a single internal instruction (micro-op) during decoding. Two program instructions can then be executed as one micro-op, reducing the overall amount of work the processor has to do. This increases the overall number of instructions that can be run within any given period of time or reduces the amount of time to run a set number of instructions. By doing more in less time, macrofusion improves overall performance and energy efficiency.
The Intel Core microarchitecture also enhances micro-op fusion – an energy-saving technique Intel first used in the Pentium M processor. In modern mainstream processors, x86 program instructions (macro-ops) are broken down into small pieces, called micro-ops, before being sent down the processor pipeline to be processed. Micro-op fusion fuses micro-ops derived from the same macro-op to reduce the number of micro-ops that need to be executed. Reduction in the number of micro-ops results in more efficient scheduling and better performance at lower power. Studies have shown that micro-op fusion can reduce the number of micro-ops handled by the out-of-order logic by more than 10%. With the Intel Core microarchitecture, the number of micro-ops that can be fused internally within the processor is extended.
Somewhat confusingly, the first Intel Core processors actually pre-dated the March 2006 announcement, having been introduced in January of that year, at the heart of the new Intel Centrino Duo Mobile Technology platform. The Intel Core Duo processor (previously codenamed Yonah) launched then was Intel’s first mobile dual-core processor built on the company’s next generation 65nm process technology. The new microarchitecture is based around an updated version of the Yonah core.
Intel chips based on the Intel Core microarchitecture started shipping in the third quarter of 2006. The first processors – for use in mobile computing, desktop systems and servers – were codenamed Merom, Conroe and Woodcrest, respectively.
- Principles of CPU architecture – logic gates, MOSFETS and voltage
- Basic structure of a Pentium microprocessor
- Microprocessor Evolution
- IA-32 (Intel Architecture 32 ) – base instruction set for 32 bit processors
- Pentium P5 microarchitecture – superscalar and 64 bit data
- Pentium Pro (P6) 6th generation x86 microarchitecture
- Dual Independent Bus (DIB) – frontside and backside data bus CPU architecture
- NetBurst – Pentium 4 7th generation x86 CPU microarchitecture
- Intel Core – 8th generation CPU architecture
- Moore’s Law in IT Architecture
- Architecture Manufacturing Process
- Copper Interconnect Architecture
- TeraHertz Technology
- Software Compatibility
- IA-64 Architecture
- Illustrated guide to high-k dielectrics and metal gate electrodes