The next step in Ethernet’s evolution was driven by the Gigabit Ethernet Alliance, formed in 1996. The ratification of associated Gigabit Ethernet standards was completed in the summer of 1999, specifying a physical layer that uses a mixture of proven technologies from the original Ethernet Specification and the ANSI X3T11 Fibre Channel Specification:
The 1000Base-X standard is based on the Fibre Channel Physical Layer and defines an interconnection technology for connecting workstations, supercomputers, storage devices and peripherals using different fibre optic and copper STP media types to support varying cable run lengths.
1000Base-T is a standard for Gigabit Ethernet over long haul copper UTP.
Gigabit Ethernet follows the same form, fit and function as its 10 Mbit/s and 100 Mbit/s Ethernet precursors, allowing a straightforward, incremental migration to higher-speed networking. All three Ethernet speeds use the same IEEE 802.3 frame format, full-duplex operation and flow control methods. In half-duplex mode, Gigabit Ethernet employs the same fundamental CSMA/CD access method to resolve contention for the shared media.
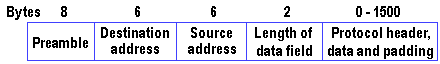
Use of the same variable-length (64- to 1514-byte packets) IEEE 802.3 frame format found in Ethernet and Fast Ethernet is key to the ease with which existing lower-speed Ethernet devices can be connected to Gigabit Ethernet devices, using LAN switches or routers to adapt one physical line speed to the other.
The topology rules for 1000Base-T are the same as those used for 100Base-T, Category 5 link lengths being limited to 100 metres and only one CSMA/CD repeater being allowed in a collision domain. Migration to 1000Base-T is further simplified both by the fact that 1000Base-T uses the same auto-negotiation system employed by 100Base-TX, and the availability of product components capable of both 100 Mbit/s and 1000 Mbit/s operation.
Fast Ethernet achieves 100 Mbit/s operation by sending three-level binary encoded symbols across the link at 125 Mbaud. 100Base-TX uses two pairs: one for transmit, one for receive. 1000Base-T also uses a symbol rate of 125 Mbaud, but it uses all four pairs for the link and a more sophisticated five-level coding scheme. In addition, it sends and receives simultaneously on each pair. Combining 5-level coding and 4 pairs allows 1000Base-T to send one byte in parallel at each signal pulse. 4 pairs x 125 Msymbols/sec x 2 bits/symbol equals 1Gbit/s.
The maximum cable length permitted in vanilla Ethernet is 2.5 km, with a maximum of four repeaters on any path. As the bit rate increases, the sender transmits the frame faster. As a result, if the same frames sizes and cable lengths are maintained, then a station may transmit a frame too fast and not detect a collision at the other end of the cable. To avoid this, one of three things has to be done:
- maintain the maximum cable length and increase the slot time (and therefore, minimum frame size)
- maintain the slot time same and decrease the maximum cable length or,
- both increase the slot time and decrease the maximum cable length.
In Fast Ethernet, the maximum cable length is reduced to a maximum of 100 metres, with the minimum frame size and slot time left intact. maintains the minimum and maximum frame sizes of Ethernet. Since it’s 10 times faster than Fast Ethernet, for Gigabit Ethernet to maintain the same slot size, the maximum cable length would have to be reduced to about 10 metres, which is impractical. Instead, Gigabit Ethernet uses a larger slot size of 512 bytes. To maintain compatibility with Ethernet, the minimum frame size is not increased, and a process known as Carrier Extension used. With this, if the frame is shorter than 512 bytes it is padded with extension symbols, special symbols, which cannot occur in the data stream.
- OSI Model
- Network Topologies
- FDDI Networking
- Token Ring Networks
- Ethernet
- Fast Ethernet
- Gigabit Ethernet
- Peer to Peer Network Architecture
- Client/Server Architecture
- P2P Networking
- Network Hardware
- NIC Cards
- Hubs and Repeaters
- Bridges
- Routers
- Network Switches
- Network Transceivers
- Cabling
- Home Networking
- Ethernet Networks
- Phone-line Networks
- Power-line Networks
- IEEE 802.11
- Wireless Networks
- Technology Comparison
I had no knowledge on Gigabit Ethernet. In your article you have given a detailed description and it was useful to me. Basically it gives a higher speed which is going to be the main attraction for its success.