Intel’s original work on the PCI standard was published as revision 1.0 and handed over to a separate organisation, the PCI SIG (Special Interest Group). The SIG produced the PCI Local Bus Revision 2.0 specification in May 1993: it took in the engineering requests from members, and gave a complete component and expansion connector definition, something which could be used to produce production- ready systems based on 5 volt technology. Beyond the need for performance, PCI sought to make expansion easier to implement by offering plug and play (PnP) hardware – a system that enables the PC to adjust automatically to new cards as they are plugged in, obviating the need to check jumper settings and interrupt levels. Windows-95, launched in the summer of that year, provided operating system software support for plug and play and all current motherboards incorporate BIOSes which are designed to specifically work with the PnP capabilities it provides. By 1994 PCI was established as the dominant Local Bus standard.
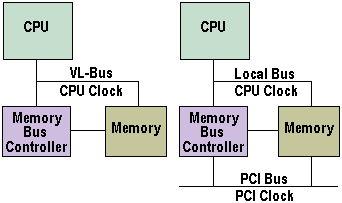
While the VL-Bus was essentially an extension of the bus, or path, the CPU uses to access main memory, PCI is a separate bus isolated from the CPU, but having access to main memory. As such, PCI is more robust and higher performance than VL-Bus and, unlike the latter which was designed to run at system bus speeds, the PCI bus links to the system bus through special bridge circuitry and runs at a fixed speed, regardless of the processor clock. PCI is limited to five connectors, although each can be replaced by two devices built into the motherboard. It is also possible for a processor to support more than one bridge chip. It is more tightly specified than VL-Bus and offers a number of additional features. In particular, it can support cards running from both 5-volt and 3.3-volt supplies using different key slots to prevent the wrong card being put in the wrong slot.
In its original implementation PCI ran at 33MHz. This was raised to 66MHz by the later PCI 2.1 specification, effectively doubling the theoretical throughput to 266 MBps – 33 times faster than the ISA bus. It can be configured both as a 32-bit and a 64-bit bus, and both 32-bit and 64-bit cards can be used in either. 64-bit implementations running at 66MHz – still rare by mid-1999 – increase bandwidth to a theoretical 524 MBps. PCI is also much smarter than its ISA predecessor, allowing interrupt requests (IRQs) to be shared. This is useful because well-featured, high-end systems can quickly run out of IRQs. Also, PCI bus mastering reduces latency and results in improved system speeds.
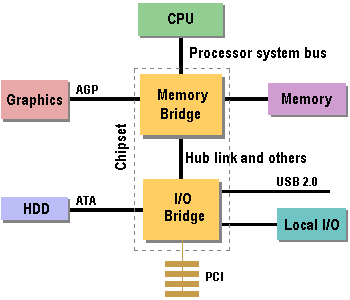
Dating from mid-1995, the main performance-critical components of the PC communicated with each other across the PCI bus. Most common amongst these PCI devices were the disk and graphics controllers, which were either mounted directly onto the motherboard or on expansion cards in PCI slots.
To PCI’s credit it has been used in applications not envisaged by the original specification writers and variants and extensions of PCI have been implemented in all of desktop, mobile, server and embedded communications market segments. However, by the late 1990s new processors and I/O devices were demanding much higher I/O bandwidth than PCI could deliver. The result was the creation of higher bandwidth buses, leading to a situation in which the PC platform supported a variety of application specific buses alongside the PCI I/O expansion bus.
Streaming data from various video and audio sources was becoming commonplace and the fact was that there was simply no baseline support for this time-dependant data within the PCI 2.2 or PCI-X specifications. The consequence was a concerted effort to agree a third-generation I/O bus to succeed PCI which, after several twists and turns, eventually culminated in the specification of the PCI Express architecture.
- What Is The System Bus?
- ISA Bus – Industry Standard Architecture
- Local Bus Interfaces
- PCI Bus Interfaces
- What is AGP and AGP Pro?
- Internal Interfaces Summary
- PCI-X Interfaces
- PCI Express Interfaces
- IDE Interfaces
- EIDE Interfaces
- Hard Disks – What IS ATA and Ultra ATA?
- Serial ATA (SATA) interface guide
- SCSI Explained – With Pictures
- SCSI Interface Evolution
- Fibre Channel Interfaces
- Hard Disks – What is Serial Storage Architecture?
- I/O Interface Standards
- How It Works: The Idea and Technology Behind USB
- IEEE 1394 Interfaces
- USB 2.0 Intefaces
- FireWire 800 Interfaces