The first DVD+RW drives had no capability to write to write-once DVD media. However, in early 2002 Verbatim became the first media maker to offer DVD+RW technology in both the ReWritable and Write-once formats. Like their DVD+RW media, the new DVD+Recordable discs were certified for 2.4x recording speed (equivalent to 3.32MBps or 22x CD-R performance).
That spring second-generation DVD+RW drives – capable of handling both types of media – began to emerge. Philips were the first off the mark, with a drive that was capable of being upgraded to read the new format via a firmware patch. Other DVD+RW Alliance optical drive manufacturers were soon to follow suit.
In October 2003, Philips Electronics and Mitsubishi Kagaku Media (better known by its Verbatim brand name) demonstrated its new dual-layer DVD recordable technology at the Ceatec Japan 2003 exhibition. The new technology virtually doubles data storage capacity on DVD+R recordable discs from 4.7GB to 8.5GB, while remaining compatible with existing DVD Video players and DVD-ROM drives.
The dual-layer DVD+R system uses two thin embedded organic dye films for data storage separated by a spacer layer. Heating with a focused laser beam irreversibly modifies the physical and chemical structure of each layer such that the modified areas have different optical properties to those of their unmodified surroundings. This causes a variation in reflectivity as the disc rotates to provide a read-out signal as with commercially pressed read-only discs.
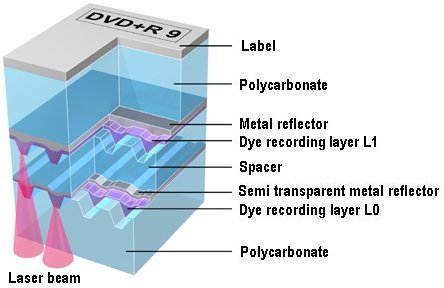
A major challenge during development – which started in 2001 – was to maintain compatibility with the DVD-ROM standard to ensure that the new dual-layer discs would be playable on commercially available DVD players. This has been achieved through the use of a thin silver-alloy as reflector material in the upper layer giving a reflectivity from the layer of at least 18% in compliance with the dual-layer DVD-ROM standard. In addition, the transmission of the upper recording layer is greater than 50% to allow for read-out and recording of the lower recording layer. This layer has high power sensitivity since the upper layer absorbs and reflects part of the incoming light. It also has a much higher reflectivity (> 50%) which after double transmission through the upper layer also results in an apparent layer reflectivity (at the disc surface) of at least 18%. These high transmission and reflectivity values have been achieved through careful optimization of the dye material and deposition, groove shapes and silver deposition. In addition to optimizing reflectivity, other parameters such as signal amplitude and tracking signals were also optimized to ensure full compatibility with current DVD standards.
The DVD+RW Alliance finalized its specification for dual-layer DVD+R media in the autumn of 2003. Dual-layer recordable technology represents an important milestone in the drive to continually improve and expand the optical data storage options available to consumers, enabling users to record 4 hours of DVD-quality video or 16 hours of VHS-quality video, without the need to turn over the disc.
With dual-layer burners, the top layer is written in the same way as by traditional single-layer burners; an organic dye film is heated by a red laser to cause fluctuations in its optical response which can then be read back as data. The second layer is written by refocusing the laser beam so that it passes through the first layer, through the partially reflective metal layer, down to the lower dye layer. The alterations in both the wavelength and the power of the laser are such as to leave the upper layer unaffected.
Using this dye-recording-film layer method, the new dual-layer DVD-R technology, shows almost the same performance as that for dual-layer DVD-ROM discs, realizing a 9.34% jitter with a 17.3% reflection rate on the first layer (L0) of a disc, and an 8.08% jitter with a 19.5% reflection rate for the second layer (L1). This means that it will be possible to play back dual-layer DVD-R discs on most existing DVD players, and that DVD recorders supporting the technology will be easily developed.
The first dual-layer burners reached the market in the summer of 2004. The principal downside of these early devices was that the added complications of dual-layer recording meant that write speeds were limited to a speed of 2.4x. This compared unfavorably with the 8x single-layer burners available at the time and the 12x and 16x burners on the horizon. A second issue was that the standard for dual-layer media requires that the same amount of data be recorded on each layer. This can result in additional time having to be spent in writing superfluous dummy data on a disc’s second layer.
- History of DVD development and birth of the DVD Forum
- DVD Formats
- DVDs – digital versatile disks – how they’re made and how they work
- DVD OSTA
- DVD File Systems
- CDR-RW Compatibility Issues
- DVD Encoding
- DVD Content Protection
- Regional codes for DVDs
- DVD-ROM
- DVD-Vdeo
- DVD DivX Codec
- DVD-Audio
- DVD Recordable Formats
- DVD-R – write once recordable DVDs
- DVD-RAM
- DVD+RW
- DVD-RW
- DVD+R
- DVD Multi-Writers