For a number of years years, CPU development had seen a shift towards delivering broader enhancements to the PC platform beyond the traditional clock speed metric. Indeed, just as there may be additional capabilities in the platform beyond the processor, there are additional features within the processor beyond clock speed.
AMD has long sought to downplay the importance of raw clock speed as a determinant of a processor’s overall level of performance and shifted to model numbers – albeit adopting a naming scheme which effectively labelled its processors with speed ratings that indicated which Intel chips they best matched up with! – some time ago. Until recently, Intel appeared happy to stick with clock speeds, presumably because their chips were clocked higher than equivalent AMD CPUs.
Things changed in the spring of 2004. In a move which it claimed would better convey the overall feature set of its processors and help end customers make more informed decisions about their PC purchase, Intel too decided to abandon its GHz-based nomenclature for its desktop and notebook products, replacing it with a naming convention based on processor numbers. In future, as well as considering raw clock speed, Intel’s processor numbers will also take account of additional important features, such as cache size, FSB speed, process technology and other significant architectural enhancements.
The result will be a processor number nomenclature system that uses a combination of the processor brand (the processor family) and a specific 3-digit number (the processor number).
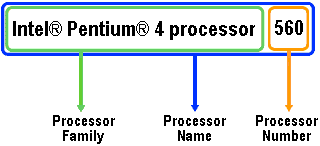
Processor numbers will be categorized in 3-digit numerical sequences such as 7xx, 5xx, or 3xx. This number plus the processor family comprise the overall processor name. Within each number sequence are specific processor numbers such as 735, 560, or 320. References to the clock speed in the processor name (as has been used in the past) will be replaced with the processor number, which now represent a broader set of features that influence the overall user experience. Processor families may also change to reflect changes in Intel’s product offerings.
At the time of the announcement, the examples of specific processor families Intel gave included:
| Desktop Processor Family | Number Sequence |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium 4 processor (including the Intel Pentium 4 processor supporting Hyper-Threading Technology and Intel Pentium 4 processor with HT Technology) | 5xx |
| Intel Celeron D processor | 3xx |
| Mobile Processor Family | Â |
| Intel Pentium M processor
(the processor component of the Intel Centrino brand) |
7xx |
| Mobile Intel Pentium 4 processor (including the Mobile Intel Pentium 4 processor supporting Hyper-Threading Technology and Mobile Intel Pentium 4 processor with HT Technology) | 5xx |
| Intel Celeron M processor | 3xx |
A higher number within a processor family can indicate more processor features, more of a specific processor feature, or a change in architecture. Note that in some cases, a higher number processor may potentially have more of one feature and less of another.
Processor numbers are intended to be used to differentiate between the relative overall features within a certain processor family (e.g. within the Intel Pentium 4 processor family) and within a numbering sequence (e.g. 550 vs 540). The digits themselves have no inherent meaning, particularly when looking across families; e.g. 710 is not better than 510 simply because 7 is greater than 5 from a numerical perspective. The numbers are aligned with different processor families and thus represent different value propositions to the end customer.
In summary, the following guidelines should be used in interpreting a processor number:
| What it is | What it isn’t |
|---|---|
| Differentiates the relative features within a processor family | A way to compare numbers across processor families |
| Indicates more features, more of a single feature, or a change in architecture | A measurement of higher performance |
| Combined with the brand, helps guide consumers in selecting the right processor | The only factor in selecting a processor |
- Pentium Architecture
- Pentium Pro
- Pentium MMX Technology
- Pentium II
- Pentium SEC
- Pentium “Deschutes
- Pentium Xeon
- Pentium III
- Pentium Tualatin
- Pentium 4
- Pentium Northwood
- Hyper-Threading Technology
- Pentium Prescott
- Pentium Processor Numbers
- Multi-Core Processors
- Pentium Smithfield
- Pentium D
- Pentium Roadmap