Also crucial to making net access viable from mobile wireless devices is WAP, the Wireless Application Protocol. WAP is a global standard and is not controlled by any single company. Ericsson, Nokia, Motorola, and Unwired Planet founded the WAP Forum in the summer of 1997 with the initial purpose of defining an industry-wide specification for developing applications over wireless communications networks. The result is an open, global specification that empowers mobile users with wireless devices to easily access and interact with information and services instantly. It works with most wireless networks – including CDMA, GSM and TDMA – and is intended to cover a wide range of wireless devices, including mobile phones, pagers, two-way radios, smartphones and PDAs.
WAP embraces and extends the previously conceived and developed wireless data protocols. Phone.com created a version of the standard HTML designed specifically for effective and cost-effective information transfer across mobile networks. Wireless terminals incorporated a HDML (Handheld Device Markup Language) micro-browser, and Phone.com’s Handheld Device Transport Protocol (HDTP) then linked the terminal to the Internet or intranet where the information being requested resided . This technology was incorporated into WAP – and renamed using WAP-related acronyms.
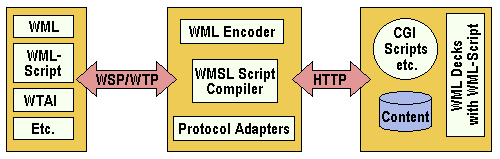
WAP also defines a wireless application environment (WAE) aimed at enabling operators, manufacturers, and content developers to develop advanced differentiating services and applications including a microbrowser, scripting facilities, email, WWW-to-mobile-handset messaging, and mobile-to-telefax access. The key utility on WAP devices is the microbrowser, which allows access to any WAP-supporting Web site. WAP’s WML (wireless markup language) uses the XML standard that is already widely used by current Web sites. However, there are important differences in the way information is organised for conventional and WAP-enabled sites. Fundamental amongst these is the fact that, unlike HTML, WML doesn’t have pages; instead, information is organised using a deck/card metaphor.
WML is designed to optimise Internet text data for delivery over limited-bandwidth wireless networks and onto small device screens. It is specifically devised to support one-hand navigation without a keyboard. WAP is scalable from two-line text displays up through graphic screens found on items such as smart phones and communicators. It also supports WMLScript. This is similar to JavaScript, but is designed to make minimal demands on system resources such as memory and CPU power. It is unlikely that WML will provide support for features such as colour, audio and video for a number years.
The process operates as follows. Someone with a WAP-compliant phone uses the in-built microbrowser to make a request in WML. This request is passed to a WAP Gateway that then retrieves the information from an Internet server either in standard HTML format or preferably directly prepared for wireless terminals using WML. If the content being retrieved is in HTML format, a filter in the WAP Gateway may try to translate it into WML. The requested information is then sent from the WAP Gateway to the WAP client, using whatever mobile network bearer service is available and most appropriate. The WAP transaction protocol (WTP) layer provides transaction support, adding reliability to the datagram service provided by WDP. The WAP session protocol (WSP) layer provides a lightweight session layer to allow efficient exchange of data between applications. The Wireless Telephony Application Interface (WTAI) is an extension to WAE designed to support Wireless Telephony Applications.
Nokia and Ericsson have written their own microbrowsers; more than 20 other vendors license the UP.Browser developed by Phone.com (formerly Unwired Planet). Much of the impetus in this area has been European, with Symbian’s EPOC OS expected to run smart-phones.
The WAP Forum is the industry association responsible for driving the standard. Members represent over 90% of the global handset market, carriers with more than 100 million subscribers, leading infrastructure providers, software developers and other organisations providing solutions to the wireless industry. Major players include AT&T, Hewlett-Packard, IBM, Intel and Symbian and Microsoft.
Nokia was the first to market with a mobile phone featuring a WAP 1.1 microbrowser – released by the WAP Forum in June 1999 – with rival wireless phone manufacturers Ericsson, Motorola, and Qualcomm following all following suit by mid-2000. WAP v1.1 had the same functionality as WAP v1.0, having incorporated refinements and clarifications to better enable compliance and interoperability testing. It also included modifications to ensure alignment with the World Wide Web Consortium’s (W3C) XHTML specification. WAP 1.2, designed to take advantage of the official WAP certification process, was released in the summer of 2000. WAP 1.3 is slated to introduce measures to assure highly secure transactions, including end-to-end security and support for wireless Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
Notwithstanding the fact that content providers need to re-author their material into WML in order for a WAP microbrowser to use it, it was thought that the promise of access to a huge untapped market of mobile customers would be sufficient for them to support WAP enthusiastically. The reality proved to be something different. One of the problems was a consequence of decks of WML information being device specific. This means that content providers to have to write different decks for different devices. The associated costs deterred many, with the result that there were fewer WAP-enabled sites than had been expected. The other big problem was performance. Even for modest applications – such as the delivery of news, stock quotes, sports results and entertainment listings, along with directory, transport, ticketing and banking enquiries – GSM’s maximum data rate of 9.6 Kbit/s proved to be inadequate. The degree of public dissatisfaction was all the more given the degree to which WAP had been over-promoted by zealous telcos.
Whether or not WAP will be able to recover from its public relations disasters of 2000 and 2001 remains to be seen. GPRS’s increased data transfer rates – to a theoretical maximum of 171.2 Kbit/s – will obviously help. However, content providers aren’t going to see their problems addressed until WAP 1.4, with its planned multi-deck emulator, is released. The timeframe for this is likely to be beyond that of GPRS deployment and by then it may be a case of too little too late. To an extent this has already happened in Japan, where the DoCoMo i-mode system (Anywhere i-mode) accesses cut-down HTML (Compact HTML) pages rather than WML decks. Launched in early 1999, i-mode has been incredibly successful in Japan with a reported 25.5 million subscribers to the service by mid-2001.