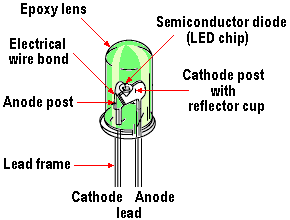
Nearly everyone is familiar with LEDs (light-emitting diodes) from their use as indicator lights and numeric displays on consumer electronic devices. The basic LED is a solid-state device that contains a chemical compound that gives off light when an electric current passes through it. It consists of a semiconductor diode chip mounted in the reflector cup of a lead frame that is connected to electrical (wire bond) wires, then encased in a solid epoxy lens. LEDs emit light when energy levels change in the semiconductor diode. This shift in energy generates photons, some of which are emitted as light. The specific wavelength of the light depends on the difference in energy levels as well as the type of semiconductor material used to form the LED chip.
LEDs are highly efficient because most of the energy they produce radiates within the visible spectrum. About 30% of the light generated inside the chip makes its way out of the brightest LEDs. Semiconductor materials have very high indices of refraction and so can trap a great deal of light when configured in a square chip. An epoxy encapsulant around the LED chip reduces the refractive index mismatch and allows more light to be emitted. There are a number of ways in which the extraction efficiency can be increased. By using transparent substrates, thick semiconductor layers and making the LED chips more spherical the amount of light escaping the chip can be reduced to a level of 4% or lower. By one estimate, the potential energy-savings from replacing the incandescent traffic signals in the USA alone with LED signals would save nearly 2.5 billion kilowatt hours annually. However, until relatively recently, their low light output and a lack of colour options have severely limited their use.
In the first LEDs to become commercially available, the semiconductor was made from a combination of three elements: gallium, arsenic and phosphorus (GaAsP). They produced a red light and appeared in the early 1960s. Other materials were investigated and, in the mid 1970s, a combination which produced green light was found. In the late 1980s, a blue-producing compound was developed but the resulting LEDs weren’t very bright. The manufacturing of LEDs uses a process know as epitaxy in which crystalline layers of different semiconductor material are grown on top of one another. Advances in epitaxial crystal growth processes resulted in the use of new compounds – such as indium gallium aluminium phosphide – enabling a bright blue LED to be developed.
LEDs have extremely fast switching times (in the order of a few hundred nanoseconds) and, with the arrival of bright blue LEDs it became possible to create matrices of red, green and blue LED clusters for use as large scale displays, with each cluster addressed as a single pixel. Though the pixel-pitch of such displays are in the region of 10mm, their high brightness, reliability, ruggedness and low power requirement make them ideal for open air displays and they are commonly seen in sporting stadia and at other public events.
LEDs come in two varieties, devices that use inorganic light emitting materials and those using organic light emitting materials. The former are known simply as LEDs, while those using organic materials are known as OLEDs (Organic LEDs). The reason that the inorganic group has the same name as the higher level group – rather than being known as ILEDs – is simply because they were developed before it was known that there were organic materials suitable for creating LEDs, and the name has stuck.
With conventional LEDs, some of the photons released by the inorganic materials are also reabsorbed by them. In contrast, with OLEDs – which produce light using the same electron/hole recombination method as LEDs – the frequencies of light absorbed by the light emitting materials lie mostly outside the visible spectrum, making them transparent when switched off and highly efficient emitters of light when switched on.
- VA – Vertically Aligned LCD Monitors
- What in the LCD is IPS!?
- ThinCRT Flat Panels
- TFT LCD Monitors
- LCD Resolutions and Picture Scaling
- Liquid Crystal Light Polarisation in LCD Monitors
- Polysilicon Flat Panels
- Plasma Flat Panels
- PALCD Flat Panels
- OLED Flat Panels
- MVA – Multi-domain Vertical Alignment in LCD Monitors
- LEP Flat Panels
- LED Flat Panels
- LCD – Liquid Crystal Displays
- IPS – In-Plane Switching LCD Monitors
- HAD Flat Panels
- Flat Panel Feature Comparisons
- FED Flat Panels
- Digital Flat Panels
- DSTN LCD monitors
- Creating Colour in LCD Displays
- Flat Panel ALiS Technology
very nice soon ill invent a new panaramic t.v screen even one you can walk thru…..