The two microdisplay technologies that have come to dominate the front projection market:
- HTPS LCD displays
- DLP displays using DMDs
both have their limitations, particularly in regard to increasing display resolutions. And this at a time when TV displays are becoming larger and high-definition content is becoming readily available, and resolution is therefore growing in importance as a measure of display quality.
LCOS can be viewed as a hybrid between the transmissive LCD and reflective DLP technologies, which attempts to combine the best features of both, while eliminating their drawbacks. In essence, it is a reflective technology that uses liquid crystals instead of individual mirrors.
Like LCD panels, LCOS panels contain thousands of cells filled with liquid crystals that twist and align in response to control voltages. However, with LCOS the liquid crystal elements are grafted directly onto a reflective silicon chip. As the liquid crystals open and close, the light is either reflected from the mirrored surface below, or blocked. This modulates the light and creates the image. Like DLP, the reflective technology means the illumination and imaging light beams share the same space, enabling the design of highly compact devices.
While LCD projectors use three LCD panels, LCOS-based projectors typically use three LCOS chips, one each to modulate light in the red, green, and blue channels. Both technologies result in the red, green, and blue components of light being delivered to the screen simultaneously.
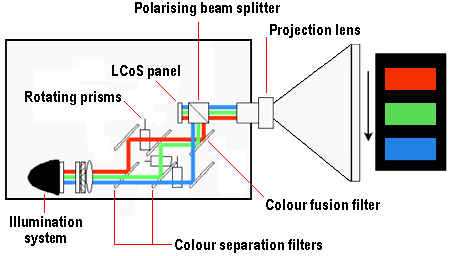
By placing the transistor drive circuitry under a pixel – out of the way of any beams of light – rather than next to it, means that the spacing between each cell (the fill factor) is smaller, further improving illumination efficiency. It also means that LCOS panels are not subject to screen door effect, which so afflicts their LCD-based counterparts.
Higher pixel density means higher resolution. LCOS devices are generally aimed at the SXGA (1365×1024) resolution class and higher and can be scaled to 1080i/p resolution (1920×1080 pixels) and beyond, without increasing the size and cost of the panel or compromising picture quality or manufacturability.
LCOS panels can be used with any kind of short-arc projection lamp, although a few front projection models have employed small xenon arc lamps. While these produce more accurate colors, they’re more expensive to operate, and don’t last nearly as long as the short-arc lamps typically found in rear-projection TVs.
Its inherent high resolution, together with the fact that LCOS projectors are not as compact as portable LCD and DLP units, means that the technology has yet to be adapted for cheaper, mass-market portable projectors. Indeed, its a very difficult technology to manufacture. The panels are manufactured on wafers, from which it has proved difficult to achieve decent yields. The challenge has been to maintain the thin walls and necessary high resolutions, and still make them in sufficient quantities for high-volume sale products.
Just how difficult this is was amply illustrated in late 2004 when both Intel and Philips closed down their LCOS development efforts. Both companies effectively decided that the amount of further investment needed to fully commercialise the technology could not be justified by the potential return on that investment. Opinion was divided as to whether their action was an indicator of a failed technology, or simply of failed methodologies.
Those believing the latter held that JVC, Sony and others were pursuing technical methods that were more likely to yield successful products. Indeed, JVC had produced the first projector using LCOS microdisplay technology as long ago as 1998 and subsequently achieved positive results by focusing its D-ILA (Direct Drive Image Light Amplifier) technology – which packs 1920×1080 pixels on a single 0.8in chip – on commercial and ultra-high end home theatre applications, enabling HD images to be displayed at their full-specification resolution.