Historically, the technology of the batteries that power notebook PCs has developed at a somewhat slower rate than other aspects of mobile computing technology. Furthermore, as batteries get better the power advantage is generally negated by increased consumption from higher performance PCs, with the result that average battery life remains fairly constant.
The chemical formulation that was common up to 1996 was Nickel-Cadmium (NiCad). As well as being environmentally unfriendly, NiCad batteries were heavy, low in capacity and prone to the dreaded memory effect. The latter was a consequence recharging a battery before it was fully discharged. The memory effect caused batteries to forget their true charge and instead provide a charge capacity much smaller and often equivalent to the average usage time prior to its recharge. Fortunately NiCad batteries are almost impossible to find in notebook PCs these days.
The replacement for Nickel-Cadmium was Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH), a more environment-friendly formulation, with a higher energy density and rather less prone to the memory effect. By 1998, the most advanced commercially available formulation was Lithium Ion (Li-Ion). Lithium Ion has a longer battery life (typically around three hours) than NiMH and does not have to be fully discharged before recharging. It is also lighter to carry. Although the price differential is narrowing, Li-Ion continues to carry a price premium over NiMH.
The main ingredient of an Li-Ion battery is lithium – not as the pure lithium metal, but in the form of atoms within the graphite forming the battery’s anode (positive terminal), as lithium-cobalt oxide or lithium-mangan oxide in the cathode (negative terminal) and as lithium salt in the battery’s electrolyte. It relies on reversible action. When being charged, some of the lithium ions usually stored in the cathode are released and make their way to the graphite (carbon) anode., where they combine into its crystalline structure. When connected to a load – such as a notebook PC – the electrochemical imbalance within the battery created by the charging process is reversed, delivering a current to the load.
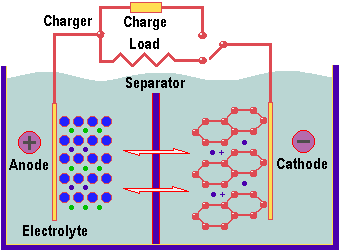
Li-Ion is used in all sorts of high-end electronic equipment, such as mobile phones and digital cameras. One downside is that it self-discharges over a few months if left on the shelf – so it requires care on the part of the user to keep it in tip-top condition.
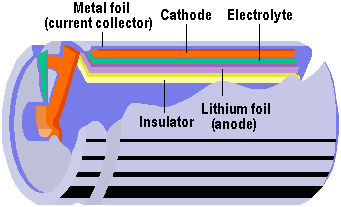
1999 saw Lithium polymer (Li-polymer) emerged as the likely battery technology of the future. Using lithium – the lightest metal on earth – this technology offers potentially greater energy densities than Li-Ion. Instead of using a liquid electrolyte – as is the case with conventional battery technologies – Li-polymer uses a solid or gel material impregnated with the electrolyte. This enables batteries to be made in almost any shape, allowing them to be placed in any of the many parts of a notebook case that would normally be filled with air. Cells are constructed from a flexible, multi-layered 100-micron thick film laminate that does not require a hard leak-proof casing. The laminate comprises five layers: a current-collecting metal foil, cathode, electrolyte, lithium foil anode and insulator.
Early lithium polymer battery prototypes proved unable to produce currents sufficiently high to make them practical. Bell core technology – named after the laboratory that invented it – is a variation on the lithium polymer theme that addresses the problem by using a mixture of liquid and polymer electrolytes able to produce higher levels of current. A number of manufacturers have licensed this technology and, in early 1999, Matsushita announced plans to commence large-scale production – 300,000 units per month – of Li-polymer batteries. Initially, the principal market for these devices will be PDAs and mobile phones, where space and weight are at a premium and value is high. Increasing use in notebook PCs is expected in the second half of 1999.
Zinc-Air technology is another emerging technology and possible competitor to Li-polymer. As the name suggests, Zinc-Air batteries use oxygen in the chemical reaction to produce electricity, thus removing the need to include metal reaction elements. Energy density by weight is therefore reduced, but volume also increases due to the need for air-breathing chambers in the battery. This reduces its appeal for small form factor devices and may relegate it to being a niche technology.
Lithium polymer is only one of several enabling technologies central to Toshiba’s view of how mobile computing will look a few years hence.
- Flat panel displays for mobile computers – laptops, notebooks and netbooks
- Battery technology for mobile computers – laptops, notebooks and webbooks
- Laptop, notebook and netbook expansion devices
- Expansion interfaces for laptops, notebooks and other mobile computers
- DynaSheet
- External keyboards for mobile computers.
- USB On-The-Go – USB technology for PDAs and mobile phones
- Guide to Kensington Slot (K-lock, Kensington Lock, Universal Security Lock) mobile device security