Although broadband has been available for some time, access for most people is still limited. At the end of 2002, it was estimated that only 46 million subscribers worldwide had broadband access, with only 17% of households in the USA being connected. Moreover, the problem isn’t one of demand, but of supply.
Worldwide Interoperability of Microwave Access (WiMAX) is a fast-emerging wide-area wireless broadband technology that shows great promise as the last mile solution for delivering high-speed Internet access to the masses. It represents an inexpensive alternative to digital subscriber lines (DSL) and cable broadband access, the installation costs for a wireless infrastructure based on IEEE 802.16 being far less than today’s wired solutions, which often require laying cables and ripping up buildings and streets.
Wireless broadband access is set up like cellular systems, using base stations that service a radius of several miles/kilometres. Base stations do not necessarily have to reside on a tower. More often than not, the base station antenna will be located on a rooftop of a tall building or other elevated structure such as a grain silo or water tower. A customer premise unit, similar to a satellite TV setup, is all it takes to connect the base station to a customer. The signal is then routed via standard Ethernet cable either directly to a single computer, or to an 802.11 hot spot or a wired Ethernet LAN.
The original 802.16 standard operates in the 10-66GHz frequency band and requires line-of-sight towers. The 802.16a extension, ratified in January 2003, uses a lower frequency of 2-11GHz, enabling nonline-of-sight connections. This constitutes a major breakthrough in wireless broadband access, allowing operators to connect more customers to a single tower and thereby substantially reduce service costs.
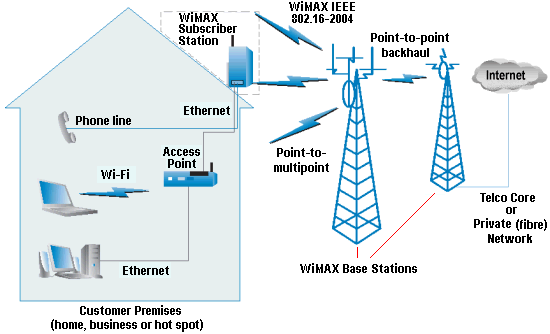
The IEEE 802.16-2004 standard subsequently revised and replaced the IEEE 802.16a and 802.16REVd versions. This is designed for fixed-access usage models. This standard may be referred to as fixed wireless because it uses a mounted antenna at the subscriber’s site. The antenna is mounted to a roof or mast, similar to a satellite television dish. IEEE 802.16-2004 also addresses indoor installations, in which case it may not be as robust as in outdoor installations.
The IEEE 802.16e standard is an amendment to the 802.16-2004 base specification and targets the mobile market by adding portability and the ability for mobile clients with appropriate adapters to connect directly to a WiMAX network.
By early 2005, delays in the start of certification testing had led to concerns that WiMAX might yet struggle to gain market share as a result. At that time, expectations were that the first standard for 802.16e to be signed off by the middle of the year, for the first commercial 802.16e products to be available in 2006 and for the first laptops integrating an Intel WiMAX chipset to appear the following year.
In the event, Intel launched its much-anticipated mobile WiMAX chip in July 2006, promising commercial trials of the chip in Europe by the end of the year. Rosedale 2 is a low-cost system-on-chip that supports IEEE 802.16-2004 and IEEE 802.16e-2005, enabling WiMAX modems for use with fixed or mobile networks. Service providers can therefore choose to immediately deploy a mobile WiMAX network, or alternatively, deploy a fixed WiMAX network now that can be easily and cost-effectively upgraded to a mobile WiMAX network.
By mid-2006, while the planned deployment of fixed WiMAX networks in selected areas of the UK was well advanced, mobile WiMAX was lagging behind in development. Many of the mobile operators such as Orange and T-Mobile were promoting the rival HSDPA or Super 3G as the technology to bring high-speed, long-range wireless connectivity to laptops and handheld devices.