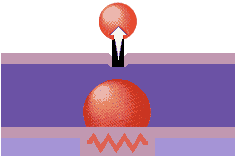
Most inkjets use thermal technology, whereby heat is used to fire ink onto the paper. There are three main stages with this method. The squirt is initiated by heating the ink to create a bubble until the pressure forces it to burst and hit the paper. The bubble then collapses as the element cools, and the resulting vacuum draws ink from the reservoir to replace the ink that was ejected. This is the method favoured by Canon and Hewlett-Packard.
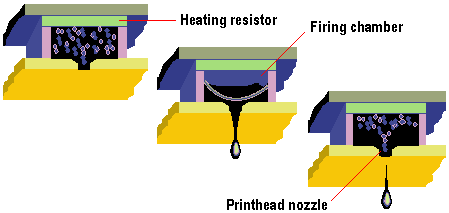
Thermal technology imposes certain limitations on the printing process in that whatever type of ink is used, it must be resistant to heat because the firing process is heat-based. The use of heat in thermal printers creates a need for a cooling process as well, which levies a small time overhead on the printing process.
Tiny heating elements are used to eject ink droplets from the print-head’s nozzles. Today’s thermal inkjets have print heads containing between 300 and 600 nozzles in total, each about the diameter of a human hair (approx. 70 microns). These deliver drop volumes of around 8 – 10 picolitres (a picolitre is a million millionth of a litre), and dot sizes of between 50 and 60 microns in diameter. By comparison, the smallest dot size visible to the naked eye is around 30 microns. Dye-based cyan, magenta and yellow inks are normally delivered via a combined CMY print-head. Several small colour ink drops – typically between four and eight – can be combined to deliver a variable dot size, a bigger palette of non-halftoned colours and smoother halftones. Black ink, which is generally based on bigger pigment molecules, is delivered from a separate print-head in larger drop volumes of around 35pl.
Nozzle density, corresponding to the printer’s native resolution, varies between 300 and 600dpi, with enhanced resolutions of 1200dpi increasingly available. Print speed is chiefly a function of the frequency with which the nozzles can be made to fire ink drops and the width of the swath printed by the print-head. Typically this is around 12MHz and half an inch respectively, giving print speeds of between 4 to 8ppm (pages per minute) for monochrome text and 2 to 4ppm for colour text and graphics.