A normal passive matrix LCD comprises a number of layers. The first is a sheet of glass coated with metal oxide. The material used is highly transparent material so as not to interfere with the quality of the image’s integrity. This operates as a grid of row and column electrodes which passes the current needed to activate the screen elements. On top of this, a polymer is applied that has a series of parallel grooves running across it to align the liquid crystal molecules in the appropriate direction, and to provide a base on which the molecules are attached. This is known as the alignment layer and is repeated on another glass plate that also carries a number of spacer beads, which maintain a uniform distance between the two sheets of glass when they’re placed together.
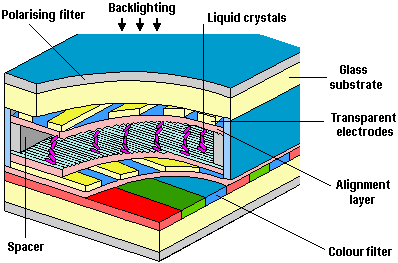
The edges are then sealed with an epoxy, but with a gap left in one corner. This allows liquid-crystal material to be injected between the sheets (in a vacuum) before the plates are sealed completely. In early models, this process was prone to faults, resulting in stuck or lost pixels where the liquid crystal material had failed to reach all parts of the screen.
Next, polarising layers are applied to the outer-most surfaces of each glass sheet to match the orientation of the alignment layers. With DSTN, or dual scan screens, the orientation of alignment layers varies between 90 degrees and 270 degrees, depending on the total rotation of the liquid crystals between them. A backlight is added, typically in the form of cold-cathode fluorescent tubes mounted along the top and bottom edges of the panel, the light from these being distributed across the panel using a plastic light guide or prism.
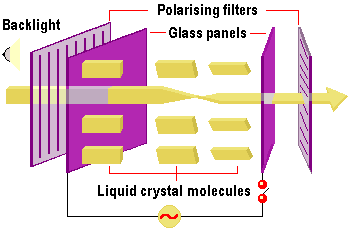
The image which appears on the screen is created by this light as it passes through the layers of the panel. With no power applied across the LCD panel, light from the backlight is vertically polarised by the rear filter and refracted by the molecular chains in the liquid crystal so that it emerges from the horizontally polarised filter at the front. Applying a voltage realigns the crystals so that light can’t pass, producing a dark pixel. Colour LCD displays simply use additional red, green and blue coloured filters over three separate LCD elements to create a single multi-coloured pixel.
However, the LCD response itself is very slow with the passive matrix driving scheme. With rapidly changing screen content such as video or fast mouse movements, smearing often occurs because the display can’t keep up with the changes of content. In addition, passive matrix driving causes ghosting, an effect whereby an area of on pixels causes a shadow on off pixels in the same rows and columns. The problem of ghosting can be reduced considerably by splitting the screen in two and refreshing the halves independently and other improvements are likely to result from several other independent developments coming together to improve passive-matrix screens.
HPD – Hybrid Passive Display
In the late 1990s, several evolutionary developments simultaneously increased dual-scan displays’ speed and contrast. HPD (hybrid passive display) LCDs, codeveloped by Toshiba and Sharp, used a different formulation of the liquid crystal material, to provide an incremental, though significant, improvement in display quality at little increased cost. A lower viscosity liquid crystal means that the material can switch between states more quickly. Combined with an increased number of drive pulses applied to each line of pixels, this improvement allowed an HPD LCD to outperform DSTN and get closer to active matrix LCD performance in a LED vs LCD test. For example, DSTN cells have a response time of 300ms, compared to an HPD cell’s 150ms and a TFT’s 25ms. Contrast is improved from the previous typical 40:1 ratio to closer to 50:1 and crosstalk has also been improved.
Another approach was a technique called multiline addressing, which analysed the incoming video signal and switched the panel as quickly as the specific image allowed. Sharp offered a proprietary version of this technique called Sharp Addressing; Hitachi’s version was called High Performance Addressing (HPA). These newer-generation panels all but eliminated ghosting, and generally delivered video quality and viewing angles that put them at least in the same ballpark as TFT screens, if still not quite in the same league.
- VA – Vertically Aligned LCD Monitors
- What in the LCD is IPS!?
- ThinCRT Flat Panels
- TFT LCD Monitors
- LCD Resolutions and Picture Scaling
- Liquid Crystal Light Polarisation in LCD Monitors
- Polysilicon Flat Panels
- Plasma Flat Panels
- PALCD Flat Panels
- OLED Flat Panels
- MVA – Multi-domain Vertical Alignment in LCD Monitors
- LEP Flat Panels
- LED Flat Panels
- LCD – Liquid Crystal Displays
- IPS – In-Plane Switching LCD Monitors
- HAD Flat Panels
- Flat Panel Feature Comparisons
- FED Flat Panels
- Digital Flat Panels
- DSTN LCD monitors
- Creating Colour in LCD Displays
- Flat Panel ALiS Technology