Cable modems offer the prospect of fast and affordable Internet access by leveraging existing broadband cable TV networks. The technology is more applicable to home than business users since it is residential areas that are more likely to be wired for cable.
The devices, manufactured by such vendors as Bay Networks and Motorola, typically are external boxes that typically attach to client PCs via Ethernet interfaces, though USB cable modems are also common. In most cases, a cable modem user is assigned a single IP address, but many cable modem providers offer additional IP addresses for multiple computers at a nominal additional charge. Alternatively, some providers allow several PCs to share a single IP address by installing a proxy server.
There are two dramatically different classes of cable modems: hybrid fibre-coax (HFC) modems, which are two-way devices that operate over HFC cable, and older one-way modems that operate over traditional coaxial TV cables. Although conventional one-way cable predominates currently, virtually all new cable construction is HFC. Regardless, any cable modem uses one or two 6MHz TV channels.
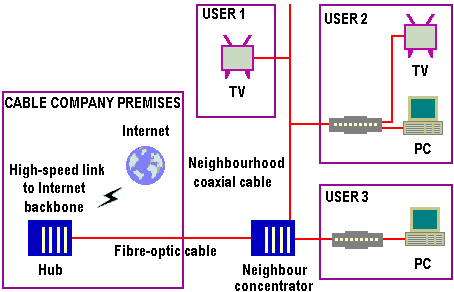
Because the cable industry’s network has a bus topology, every cable modem in a neighborhood shares access to a single coaxial cable backbone. While it’s possible for sharing to slow throughput, this can be avoided by a good design with the help of professional Structured Network Cabling Services just like the ones at structured cabling San Francisco. A two-way cable modem provides links to and from the Internet. A one-way cable modem requires a dial-up modem for uploads. A neighborhood concentrator combines data from several neighborhood cables and communicates with a larger router, or hub, at the cable company’s main plant via – typically via a fibre-optic cable link. The hub sends TCP/IP data from each modem to the Internet via a high-speed leased line or private backbone.
While local cable companies provide the modem as part of its service, interoperability between modems isn’t an issue. However, this will become so in the future, when subscribers will be able to buy and own their own cable modem. One ray of hope is an Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) working group committee, 802.14, that’s trying to define a common media-access control scheme for sending data over cable. The committee is selecting the best elements from among 17 different proposals and hoped to have its recommendations finished by the end of 1998. A number of vendors are also working together to ensure product interoperability.
The cable modem’s function is to modulate and demodulate the cable signal into a stream of data; and the similarity with analogue modems ends there. Cable modems also incorporate a tuner (to separate the data signal from the rest of the broadcast stream); parts from network adapters, bridges, and routers (to connect to multiple computers); network-management software agents (so the cable company can control and monitor its operations); and encryption devices (so data isn’t intercepted or sent to a wrong destination by mistake).
Each cable modem has an Ethernet port that connects to the computer (or network) on one side and to the cable connection on the other. As far as the PC is concerned, it’s hooked directly to the Internet via an Ethernet cable. There are no phone numbers to dial and no limitations on serial-port throughput (as is the case with ISDN modems).
Cable has a number of practical disadvantages compared with the rival xDSL technology. Two of the most obvious concern location: first, not all homes are yet wired for cable TV, and those in rural areas may never be. Homes that are cabled up, however, often have a contended service, so performance and speed will degrade the greater the number of subscribers in a given locale. Second, many homes hooked up to cable are more likely to have their PC located in proximity to a telephone jack than to a TV or existing cable drop, but this is much less of a problem since the advent of wireless routers.
For many home users cable offers the prospect of fast Internet access at an affordable price. Virgin Internet UK began a groundbreaking 50 Mbit/s home service in 2008, which although at a premium rate was nonetheless affordable for such speeds.
- ISDN
- xDSL Digital Subscriber Line technologies – ADSL, HDSL, VDSL
- An Overview of ADSL – What It Is and How It Works
- Glite
- ADSL2
- ADSL2+ | ADSL2Plus | ITU G.992.5
- xDSL Variants
- ADSL Implimentation
- Wires-Only ADSL – Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line
- Cable Modems – for cable Internet connections
- A Description and Explanation of Satellite Broadband and How It Works