Memory manufacturer SanDisk introduced CompactFlash (CF) in 1994 as a small format memory card, which used the existing PCMCIA-ATA specification to communicate with PCs. These cards are roughly a quarter the size of a PC Card and use flash technology that allows data to be stored indefinitely, without any power to the card.
CF cards come in two sizes, Type I and Type II. The only difference between the types is the thickness of the cards, 3.3mm for Type I and 5mm for Type II. This reflects the fact that there were different thickness PC Cards and slots at the time, and this allowed CF cards to take advantage of the thicker Type II PC Card slots. However, these thicker versions are now obsolete.
CF had been devised primarily for devices smaller than PCs such as digital cameras and PDAs, and other memory manufacturers were attracted to the format by the standard interface. As CF slots began appearing on cameras and PDAs, as well as other more specialized devices, prices came down. At the same time, the available RAM on the cards increased until cards of 32Gb and more became available. The CF standard allows for a theoretical maximum size of 137Gb.
The CF specifications are regularly being updated to take account of increased hard disk sizes, memory access speeds and upgrades to hard disk specifications such as IDE Ultra DMA 133 and SATA
Because all types of CF cards can operate at both 3.3 and 5V, and they conform to the PCMCIA-ATA and TrueIDE functionality (compatible with ATA/ATAPI-4 disk interface specs) they can use almost any PC operating system and file system. This has helped them gain acceptance quickly, although it should be noted that although they can be formatted with almost any file system, the cameras and PDAs will normally be only able to use FAT or FAT32. In fact, it is a wise precaution to only format the cards in the device that you’ll be using them for rather than from a PC.
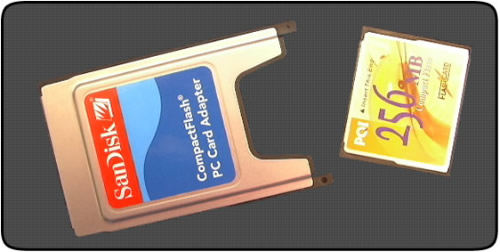
The use of the PCMCIA-ATA specification also means that simple and cheap adapters can be made using a shell of a PCMCIA card. A CF card slips into one end of the adapter and the other end goes into an ordinary PCMCIA slot, enabling the CF card to be accessed just like a floppy. The adaptor only needs wiring inside to convert the physical CF interface to PCMCIA format, there’s no need for chips or other intelligence, which keeps the cost down.
There are also stand-alone USB card readers that will accept CF card and many modern PC’s have a multi-format card reader built-in in lieu of a floppy drive. One advantage of the CF format is that the cards can’t be inserted the wrong way round, not something that can be said of some other formats.
CF cards are still very much in use despite smaller card formats appearing on the market to cater for newer and even smaller devices. The format has retained its supremacy in the professional digital camera market and delivers memory at a good price. CF cards have also carved out a niche market in replacing hard disks in embedded devices. Their power consumption is around 5% that of hard disks and they have no moving parts, making them perfect for specialist applications. Compared to hard disks they are more reliable, more shock resistance and produce less heat, all of which is important for embedded devices.
- Hard disk (hard drive) construction
- Hard Disk (hard drive) Operation
- Hard disk (hard drive) format – the tracks and sectors of the hard disk
- File systems (FAT, FAT8, FAT16, FAT32 and NTFS) explained
- Hard Disk (Hard Drive) Performance – transfer rates, latency and seek times
- Hard Disk AV Capability
- Hard Disk Capacity
- Hard Disk Capacity Barriers
- Hard Disk MR Technology
- Hard Disk GMR Technology
- Hard Disk Pixie Dust
- Hard Disk Longitudinal Recording
- Hard Disk Perpendicular Recording
- RAID – Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks
- Hard Disk SMART Drives
- Hard Disk MicroDrives
- Hard Disk OAW Technology
- Hard Disk PLEDM
- Hard Disk Millipede
- Guide to Western Digital’s GreenPower hard drive technology
- Solid state hard drive (SSD) technology guide