Giant Magneto-Resistive (GMR) head technology builds on existing read/write technology found in TFI and anisotropic MR, producing heads that exhibit a higher sensitivity to changing magnetisation on the disc and work on spin-dependent electron scattering. The technology is capable of providing the unprecedented data densities and transfer rates necessary to keep up with the advances in processor clock speeds, combining quantum mechanics and precision manufacturing to give areal densities that are expected to reach 10Gbits/in2 and 40Gbits/in2 by the years 2001 and 2004 respectively.
In MR material, e.g. nickel-iron alloys, conduction electrons move less freely (more frequent collisions with atoms) when their direction of movement is parallel to the magnetic orientation in the material. This is the MR effect, discovered in 1988. When electrons move less freely in a material, the material’s resistance is higher. GMR sensors exploit the quantum nature of electrons, which have two spin directions-spin up and spin down. Conduction electrons with spin direction parallel to a film’s magnetic orientation move freely, producing low electrical resistance. Conversely, the movement of electrons of opposite spin direction is hampered by more frequent collisions with atoms in the film, producing higher resistance. IBM has developed structures, identified as spin valves, in which one magnetic film is pinned. This means its magnetic orientation is fixed. The second magnetic film, or sensor film, has a free, variable magnetic orientation. These films are very thin and very close together, allowing electrons of either spin direction to move back and forth between these films. Changes in the magnetic field originating from the disk cause a rotation of the sensor film’s magnetic orientation, which in turn, increases or decreases resistance of the entire structure. Low resistance occurs when the sensor and pinned films are magnetically oriented in the same direction, since electrons with parallel spin direction move freely in both films.
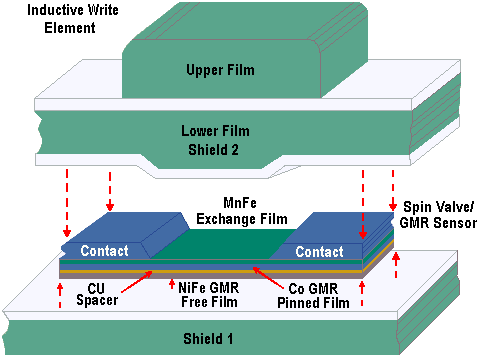
Higher resistance occurs when the magnetic orientations of the sensor and pinned films oppose each other, because the movement of electrons of either spin direction is hampered by one or the other of these magnetic films. GMR sensors can operate at significantly higher areal densities than MR sensors, because their percent change in resistance is greater, making them more sensitive to magnetic fields from the disk.
Current GMR hard disks have storage densities of 4.1Gbit/in2, although experimental GMR heads are already working at densities of 10Gbit/in2. These heads have a sensor thickness of 0.04 microns, and IBM claims that halving the sensor thickness to 0.02 microns – with new sensor designs – will allow possible densities of 40Gbit/in2. The advantage of higher recording densities is that disks can be reduced in physical size and power consumption, which in turn increases data transfer rates. With smaller disks for a given capacity, combined with lighter read/write heads, the spindle speed can be increased further and the mechanical delays caused by necessary head movement can be minimized.
IBM has been manufacturing merged read/write heads which implement GMR technology since 1992. These comprise a thin film inductive write element and a read element. The read element consists of an MR or GMR sensor between two magnetic shields. The magnetic shields greatly reduce unwanted magnetic fields coming from the disk; the MR or GMR sensor essentially sees only the magnetic field from the recorded data bit to be read. In a merged head the second magnetic shield also functions as one pole of the inductive write head. The advantage of separate read and write elements is both elements can be individually optimized. A merged head has additional advantages. This head is less expensive to produce, because it requires fewer process steps; and, it performs better in a drive, because the distance between the read and write elements is less.
- Hard disk (hard drive) construction
- Hard Disk (hard drive) Operation
- Hard disk (hard drive) format – the tracks and sectors of the hard disk
- File systems (FAT, FAT8, FAT16, FAT32 and NTFS) explained
- Hard Disk (Hard Drive) Performance – transfer rates, latency and seek times
- Hard Disk AV Capability
- Hard Disk Capacity
- Hard Disk Capacity Barriers
- Hard Disk MR Technology
- Hard Disk GMR Technology
- Hard Disk Pixie Dust
- Hard Disk Longitudinal Recording
- Hard Disk Perpendicular Recording
- RAID – Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks
- Hard Disk SMART Drives
- Hard Disk MicroDrives
- Hard Disk OAW Technology
- Hard Disk PLEDM
- Hard Disk Millipede
- Guide to Western Digital’s GreenPower hard drive technology
- Solid state hard drive (SSD) technology guide