For several months after the Pentium 4 began shipping in late 2000 the leadership in the battle to have the fastest processor on the market alternated between Intel and rival AMD, with no clear winner emerging. However, towards the end of 2001 AMD had managed to gain a clear advantage with its Athlon XP family of processors.
Intel’s response came at the beginning of 2002, in the shape of the Pentium 4 Northwood core, manufactured using the 0.13-micron process technology first deployed on the company’s Tualatin processor in mid-2001. The transition to the smaller fabrication technology represents a particularly important advance for the Pentium 4. When it was originally released as a 0.18-micron processor, it featured a core that was almost 70% larger than the competition. A larger core means that there is a greater chance of finding defects on a single processor thus lowering the yield of the part. A larger core also means that fewer CPUs can be produced per wafer also making the CPU a very expensive family member.
The 0.13-micron Northwood core addresses this issue. Compared with the original 0.18-micron Willamette die’s surface area of 217mm2, the Northwood’s is a mere 146mm2. What this means is that on current 200mm wafers, Intel is now able to produce approximately twice as many Pentium 4 processors per wafer as was possible on the 0.18-micron process.
In fact, architecturally the new Northwood core doesn’t differ much at all from its predecessor and most of its differences can be attributed to the smaller process technology. First off, Intel exploited the opportunity this gave them to increase the transistor count – up to 55 million from 42 million – by increasing the size of the Level 2 cache from 256KB to 512KB.
The use 0.13-micron technology also allowed the Vcore to be reduced from 1.75V to 1.5V, thereby significantly influencing heat dissipation. The maximum heat dissipation of the older Pentium 4 processors working at 2GHz was 69W; by contrast, the new Pentium 4 Northwood working at the same clock frequency dissipates only 41W of heat.
The Northwood processors released in early 2002 were available in two speeds; 2.0GHz and 2.2GHz. In order to differentiate it from its older 0.18-micron counterpart, the former is referred to as a Pentium 4 2A. 2.26GH and 2.4GHz versions – using a faster Quad Pumped Bus working at 533MHz – are expected by spring 2002 and the 3GHz milestone is likely to be reached before the end of the year.
The new core completed the transition from the Socket 423 interface used by earlier Pentium 4s to the Socket 478 form factor, all Northwood versions being available only in the latter format. It is expected that Socket 478 to Socket 423 converters will be available to enable owners of older motherboards to upgrade to the newer processors. Socket 478 motherboards may be coupled with either Intel’s i850 (DRDRAM) chipset or DDR SDRAM supporting chipsets such as the i845 and rival offerings from SiS and VIA.
In the autumn of 2002, the Pentium 4 became the first commercial microprocessor to operate at 3 billion cycles-per-second. The 3.06GHz Pentium 4 was also significant in that it marked the introduction of Intel’s innovative Hyper-Threading (HT) Technology to the desktop arena. In fact, HT Technology has been present on earlier Pentium 4 processors. It hasn’t been enabled before because the system infrastructure necessary to take full advantage of the technology – chipset support, motherboards that meet the required power and thermal specifications, the necessary BIOS, driver and operating system support – hasn’t been in place previously.
Pioneered on Intel’s advanced server processors, HT Technology enables a PC to work more efficiently by maximising processor resources and enabling a single processor to run two separate threads of software simultaneously. For multitasking environments, the net result is an improved level of performance which manifests itself in appreciably better system responsiveness.
Pentium 4 performance received a significant boost in the spring of 2003 with the announcement of technical innovations that both accelerated the speed at which data flows between the computer’s processor and system memory and also doubled the computer’s networking bandwidth.
The new processor was an excellent illustration of how ramping up clock speeds is not the only way to increase performance. Increasing the fastest system bus speed from 533MHz to 800MHz enables information to be transmitted within the system up to 50% faster than in the chip’s previous version. Furthermore, by providing support for dual-channel DDR400 memory, the new i875P/i865 chipset platform – announced at the same time – provides the increased memory bandwidth architecture necessary for the faster system bus to be fully exploited, the 6.4GBps of memory bandwidth provided by dual-channel DDR400 memory being perfectly balanced with the 800MHz FSB.
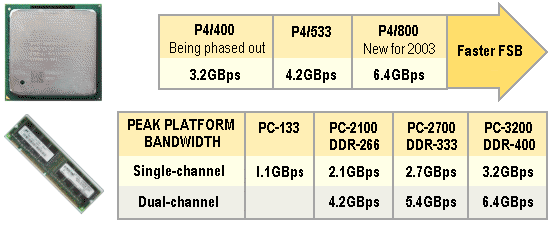
The first of the 800MHz FSB CPUs was the Pentium 4 3.0C – C designating 800MHz FSB support, much like the B designation of 533MHz FSB support in the early days of the first 533MHz FSB Pentium 4 processors. This was 66MHz less than Intel’s previous fastest Pentium 4. Lower clocked versions still were introduced over the succeeding period, culminating in the release of a 3.2GHz model in the summer of 2003. This was expected to be the last 0.13-micron Northwood processor before the debut of new Prescott core – produced using a 90 nanometre process (0.09 microns) – in the final quarter of 2003.
- Pentium Architecture
- Pentium Pro
- Pentium MMX Technology
- Pentium II
- Pentium SEC
- Pentium “Deschutes
- Pentium Xeon
- Pentium III
- Pentium Tualatin
- Pentium 4
- Pentium Northwood
- Hyper-Threading Technology
- Pentium Prescott
- Pentium Processor Numbers
- Multi-Core Processors
- Pentium Smithfield
- Pentium D
- Pentium Roadmap